Multi-Colouring Type 1 eg 1. From the Start This rule is shared with Simple Colouring.
Simple Coloring Singles Chains Strategy Sudoku
Whenever you enter a number use the current color ie.
Sudoku simple coloring rule 2. If c23 then without even looking at the grid e2 cannot be 3. The Rule is as follows. Its the same principle as the first rule but we are looking for two coloured occurrences of X in the same unit row column or box as opposed the two of the colour in the same cell.
Load Example or. It is easy to see that there are a number of conjugate relationships allowing alternate coloring in a chain. You have to find this chain and mark which candidate 9 is eliminated.
When a candidate is possible in a certain block and rowcolumn and it is not possible anywhere else in the same block then it is also not possible anywhere else in the same rowcolumn. Looking at row C which also contains the naked twin the rule eliminates 2 from square Cc and a 4 must go there. We would like to show you a description here but the site wont allow us.
Enter numbers into the blank spaces so that each row column and 3x3 box contains the numbers 1 to 9 without repeats. When you find a chain of conjugate pairs you might be able to use simple coloring to remove candidates. Simple Colors Simple Colors is a subtype of coloring which only uses 2 colors.
These candidates have a strong link. Since the pair has an eitheror relationship you can give each candidate a different color. Every Sudoku has a unique solution that can be reached logically.
The naive approach is to generate all possible configurations of numbers from 1 to 9 to fill the empty cells. Dont Repeat Any Numbers As you can see in the upper left square circled in blue this square already has 7 out of the 9 spaces filled in. Try every configuration one by one until the correct configuration is found ie.
The pen chosen in step 5. The locked candidate rule form 2. Sudoku Rule 2.
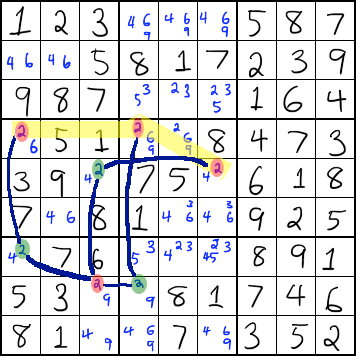
The only numbers missing from the square are 5. In this Sudoku weve looking at number 7 and labelled two chains A. Starting with the cell R2C2 which Ive arbitrarily colored green it has 2 conjugates - cells R6C2 since there are only 2 candidate 9s in Column 2 and cell R2C3 since there are only 2 candidate 9s in row 2 which Ive colored blue.
How it works 1 The following example demonstrates the principle. There is a ridiculously long chain using the number 9 on this board which contains twelve links. Repeat this process until you can find no more preemptive sets or until the Sudoku rule is violated or there is a cell whose markup is empty contains no numbers.
How to use Simple Coloring. Get out your pencil and try these puzzles for all levels. Create your own Sudoku Ebook.
If A shares a unit with B and B- then A must be the false candidate since either B or B- must be true. If two Nodes in the Chain belong to the same region Row Column or Square and if they have the same color then this color can not be the solution because a candidate can not be the solution for two cells in the same. Try your hand at easy medium or hard brainteasers.
Play Offline with Web Sudoku Deluxe Download for Windows and Mac. Next start from one of the colored numbers and look for a conjugate pair that it chains with. 3D Medusa Rule 2.
Each puzzle is generated randomly so there is an almost limitless selection. It uses the second rule so. Guides for new and experienced players.
Demonstration and explanation of how to use Two Colors to map out a network of Conjugate Pairs and then eliminate Candidates that are proven to be False by. Not only does Simple Sudoku make challenging puzzles it also provides tools to help solve them - removing the drudgery but not the fun. Try to use methods 2 and 3 again if you were able to cross out numbers from the markups of any cells.
The user can also choose between five levels of complexity - from Easy to Extreme. So looking at square Da the naked twin rule excludes 2 from occurring here because we have just shown that region Ca must have a 2 in either Ca or Cb. SIMPLE COLORING TWICE IN A UNIT.
Once all the singles have been found I usually start marking. Easy Medium Hard Evil Try Variations Download Deluxe. The logic is colorfully highlighted but here is an explanation.
The alternating colours have been marked. If tiles are tripping you up watch this simple strategy. The history of your favorite numbers game.
Load Example or. Since 3s in column e are limited to e2e4e5 - If e23 then 3s must exist within e45. Start with one conjugate pair.
When a row column or box contains only 2 candidates for a digit one of them must be true and the other must be false. For every unassigned position fill the position with a number from 1 to 9. All the candidates for digit 3 are highlighted.
Keeping track of possible values for blank cells candidates providing filters and color markers are. As Da is now left with a single possibility a 1 can be safely allocated there. Since 3s in column c are limited to c2c6 - If c63 then c23.
If c63 then clearly d6 cannot be 3.
Sudoku Simple Coloring Strategy Explained
Simple Coloring Type Ii Sudoku Tutorial 32 Youtube
Sudoku 6x6 Sudoku Sudoku Puzzles Brain Training Games
Simple Coloring Singles Chains Strategy Sudoku
Simple Coloring Singles Chains Strategy Sudoku
Free Printable Sudoku Puzzles You Can Solve Today Sudoku Puzzles Sudoku Sudoku Printable
0 Comments